Yeast Infection – Genital Candidiasis
What is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis is a curable overgrowth of a type of fungus (yeast) called Candida. Candida is usually and normally present in the body in small amounts. However, sometimes an imbalance occurs in the body that causes overgrowth of this yeast. For example, a change in the normal acidity/pH of the vagina, or hormonal changes, or certain medications like antibiotics or birth control pills can cause Candida overgrowth.
There are several types of candidiasis, depending on where the overgrowth occurs:
- Candida overgrowth in the mouth or throat is called thrush.
- Candida overgrowth on the genitals is called a yeast infection.
- Candida overgrowth on a baby’s bottom is called a diaper rash.
- Candida overgrowth in the blood is called candidemia.
Use our dermatology search engine to screen your STDs
Yeast Infection – Genital Candidiasis
Yeast infections are candida overgrowth in the genitals. Both men and women can get yeast infections. Almost 75% of all women have had at least 1 yeast infection in their lifetime.
How Dangerous are Yeast Infections?
Yeast infections are usually not dangerous if treated.
Use our dermatology search engine to screen your STDs
What Causes Yeast Infections / How are Yeast Infections Spread?
Candida is usually and normally present in the body in small amounts, such as the skin, genitals, mouth, throat, and blood. Typically, yeast infections are caused by your own overgrowth of the candida that is normally present in the body. It is uncommon for yeast infections to be spread from another person through sexual intercourse.
Signs of Yeast Infection
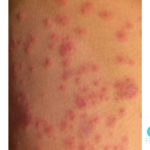
Women – Women with yeast infections often experience genital itching, soreness, burning, and/or discharge that looks like cottage cheese. It may be painful to have sexual intercourse.
Men – Men with yeast infections often experience itchy or burning rash on their penises.
How are Yeast Infections Diagnosed?
Yeast infections are usually diagnosed by the patient’s symptoms, and are confirmed by looking at a sample of vaginal discharge or secretions under a microscope.
Use our dermatology search engine to screen your STDs
How are yeast infections treated?
Luckily, yeast infections are completely curable with over-the-counter antifungal medication, usually taken for 2 weeks. This medication will kill the fungus. The medicine can either be a cream or a suppository that you place inside the vagina or on the penis. Either works equally well.
Sometimes your doctor may recommend a single dose of fluconazole (Diflucan). It is important that you see a doctor first and be diagnosed correctly before treating yourself with over-the-counter medication, because your symptoms may be due to a different infection (for example, a urinary tract infection). If the medications do not work or if the yeast infection keeps coming back, you may need new antifungal medication – see your doctor.
Use our dermatology search engine to screen your STDs
How can you prevent yeast infections?
There is no vaccine for yeast infections, and yeast infections are fairly common. Yeast likes to live in moist environments, so keeping a dry environment around your genitals can help prevent yeast infections. For example, wearing cotton underwear helps to absorb any moisture, as opposed to nylon or other synthetic fabrics. Avoid wearing tight-fitting pants, and change out of wet clothes (from swimming, sweating at the gym, the rain, etc) as soon as possible.
Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom, and don’t use douches or scented sprays because they can disrupt the normal balance of bacteria and fungus. Douches can spread the infection further up your body into the uterus. Having a balanced diet and minimizing stress will also be helpful in keeping your body in balance.